Page 9 - machining_titanium_05_2019
P. 9
MACHINABILITY OF TITANIUM
There a widespread belief that titanium is like austenitic stainless steel in
terms of its machinability. This may be true when relating to commercially pure
titanium and also, with some assumption, α- or even α-β-alloys; however, it is
fundamentally wrong with respect to the treated β- and near-β- alloys.
In general, titanium alloys (which we will refer to as titanium and specify their composition, grade MACHINABILITY OF TITANIUM
and properties separately where necessary) are hard-to-machine materials and their machinability
depends on various factors: chemical composition, hardness, method of treatment.
The main difficulties in cutting titanium are the following:
• Intensive heat generation leads to excessive adhesive wear of cutting edge.
• Low heat conductivity results in poor heat transfer and slowing heat dissipation
down. Therefore, cutting edge experiences considerable thermal loading.
• “Springiness” of titanium due to low modulus of elasticity contributes to
vibrations and worsens machining accuracy and surface finish.
The mentioned factors significantly reduce tool life and affect performance.
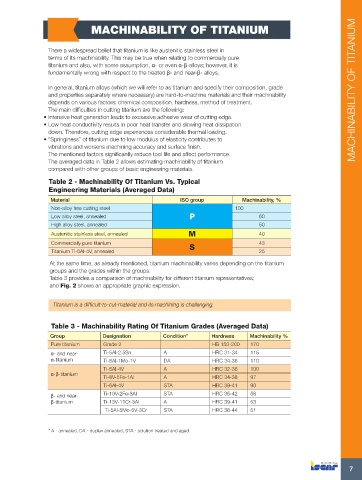
The averaged data in Table 2 allows estimating machinability of titanium
compared with other groups of basic engineering materials.
Table 2 - Machinability Of Titanium Vs. Typical
Engineering Materials (Averaged Data)
Material ISO group Machinability, %
Non-alloy free cutting steel 100
Low alloy steel, annealed P 60
High alloy steel, annealed 50
Austenitic stainless steel, annealed M 40
Commercially pure titanium S 43
Titanium Ti-6Al-4V, annealed 25
At the same time, as already mentioned, titanium machinability varies depending on the titanium
groups and the grades within the groups.
Table 3 provides a comparison of machinability for different titanium representatives;
and Fig. 2 shows an appropriate graphic expression.
Titanium is a difficult-to-cut-material and its machining is challenging.
Table 3 - Machinability Rating Of Titanium Grades (Averaged Data)
Group Designation Condition* Hardness Machinability %
Pure titanium Grade 2 HB 150-200 170
α- and near- Ti-5Al-2.5Sn A HRC 31-34 115
α-titanium Ti-8Al-1Mo-1V DA HRC 34-36 110
Ti-6Al-4V A HRC 32-36 100
α-β-titanium Ti-8V-5Fe-1Al A HRC 34-38 97
Ti-6Al-4V STA HRC 39-41 90
β- and near- Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al STA HRC 35-42 56
β-titanium Ti-13V-11Cr-3Al A HRC 39-41 53
Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr STA HRC 36-44 51
* A - annealed, DA - duplex annealed, STA - solution treated and aged
7