Page 40 - THREADING CATALOG
P. 40
USER GUIDE
THREAD TURNING Basic Dimensions of Square Shank Tools
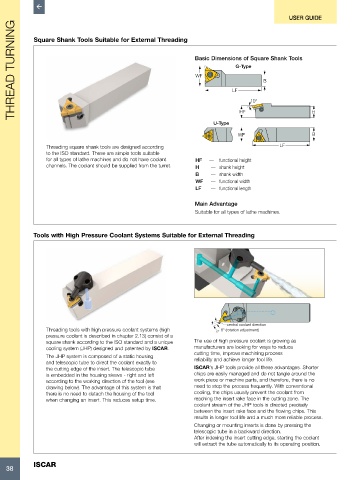
Square Shank Tools Suitable for External Threading
G-Type
WF
B
LF
U-Type HF 10° H
WF B
Threading square shank tools are designed according LF
to the ISO standard. These are simple tools suitable
for all types of lathe machines and do not have coolant HF — functional height
channels. The coolant should be supplied from the turret. H — shank height
B — shank width
WF — functional width
LF — functional length
Main Advantage
Suitable for all types of lathe machines.
Tools with High Pressure Coolant Systems Suitable for External Threading
central coolant direction
Threading tools with high pressure coolant systems (high 4° 8° (rotation adjustment)
pressure coolant is described in chapter 2.13) consist of a
square shank according to the ISO standard and a unique The use of high pressure coolant is growing as
cooling system (JHP) designed and patented by ISCAR. manufacturers are looking for ways to reduce
The JHP system is composed of a static housing cutting time, improve machining process
and telescopic tube to direct the coolant exactly to reliability and achieve longer tool life.
the cutting edge of the insert. The telescopic tube ISCAR’s JHP tools provide all these advantages. Shorter
is embedded in the housing skews - right and left chips are easily managed and do not tangle around the
according to the working direction of the tool (see work piece or machine parts, and therefore, there is no
drawing below). The advantage of this system is that need to stop the process frequently. With conventional
there is no need to detach the housing of the tool cooling, the chips usually prevent the coolant from
when changing an insert. This reduces setup time. reaching the insert rake face in the cutting zone. The
coolant stream of the JHP tools is directed precisely
between the insert rake face and the flowing chips. This
results in longer tool life and a much more reliable process.
Changing or mounting inserts is done by pressing the
telescopic tube in a backward direction.
After indexing the insert cutting edge, starting the coolant
will extract the tube automatically to its operating position.
ISCAR
38