Page 28 - THREADING CATALOG
P. 28
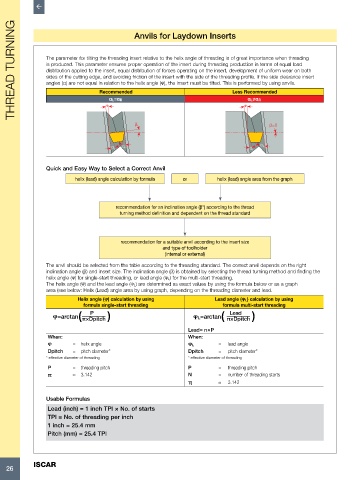
THREAD TURNING The parameter for tilting the threading insert relative to the helix angle of threading is of great importance when threading
Anvils for Laydown Inserts
is produced. This parameter ensures proper operation of the insert during threading production in terms of equal load
distribution applied to the insert, equal distribution of forces operating on the insert, development of uniform wear on both
sides of the cutting edge, and avoiding friction of the insert with the side of the threading profile. If the side clearance insert
angles (α) are not equal in relation to the helix angle (φ), the insert must be tilted. This is performed by using anvils.
Less Recommended
Recommended
αL=αR
φ
β φ αL≠αR β =0
α R
α R
α L
α L
Quick and Easy Way to Select a Correct Anvil
helix (lead) angle calculation by formula or helix (lead) angle area from the graph
recommendation for an inclination angle (β°) according to the thread
turning method definition and dependent on the thread standard
recommendation for a suitable anvil according to the insert size
and type of toolholder
(internal or external)
The anvil should be selected from the table according to the threading standard. The correct anvil depends on the right
inclination angle (β) and insert size. The inclination angle (β) is obtained by selecting the thread turning method and finding the
helix angle (φ) for single-start threading, or lead angle (φ L) for the multi-start threading.
The helix angle (φ) and the lead angle (φ L) are determined as exact values by using the formula below or as a graph
area (see below: Helix (Lead) angle area by using graph, depending on the threading diameter and lead.
Helix angle (φ) calculation by using Lead angle (φ L) calculation by using
formula single-start threading formula multi-start threading
( π×Dpitch ) π×Dpitch )
Lead
P
φ=arctan φ =arctan (
L
Lead= n×P
When: When:
φ = helix angle φ L = lead angle
Dpitch = pitch diameter* Dpitch = pitch diameter*
* effective diameter of threading * effective diameter of threading
P = threading pitch P = threading pitch
π ≈ 3.142 N = number of threading starts
π ≈ 3.142
Usable Formulas
Lead (inch) = 1 inch TPI × No. of starts
TPI = No. of threading per inch
1 inch = 25.4 mm
Pitch (mm) = 25.4 TPI
ISCAR
26